What is Big Data? Complete Guide with Examples, Graphs, and Tables
In the last decade, the term Big Data has become one of the most significant buzzwords across industries. From social media platforms collecting user preferences to healthcare organizations analyzing patient records, and from e-commerce companies predicting consumer behavior to governments managing census data, the role of Big Data is undeniable. But what exactly is Big Data? Why is it important? How can organizations use it to make better decisions and improve efficiency? This article provides a comprehensive explanation of Big Data, covering its definition, characteristics, importance, benefits, challenges, and real-world applications.
What is Big Data?
Big Data refers to extremely large, complex, and diverse data sets that are difficult to manage, store, process, and analyze using traditional data management tools. It encompasses structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data generated at high velocity from multiple sources, including digital platforms, sensors, mobile devices, social networks, and business transactions. In simpler terms, Big Data represents the massive volume of information generated every second by individuals, organizations, and machines, which when properly analyzed can provide valuable insights for decision-making.
Characteristics of Big Data (The 5 V’s)
The most common way to understand Big Data is through the 5 V’s model:
-
Volume – Refers to the sheer amount of data generated daily. For example, over 500 million tweets are sent every day on Twitter.
-
Velocity – The speed at which data is generated and processed. Think of live-streaming data from financial markets or real-time GPS tracking.
-
Variety – Data comes in different forms, including text, video, images, audio, and numerical values.
-
Veracity – The accuracy and trustworthiness of the data. Since not all data is reliable, organizations must filter out noise.
-
Value – The ultimate goal is to derive meaningful insights and benefits from data analysis.
Table 1: Examples of Big Data Across Different Industries
| Industry | Source of Big Data | Source of Big Data |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Patient records, medical imaging, sensors | Predicting disease outbreaks, diagnosis |
| Retail & E-commerce | Transaction data, customer reviews, social media | Personalized product recommendations |
| Banking & Finance | Stock market feeds, fraud detection systems | Risk management, fraud detection |
| Manufacturing | IoT devices, machinery sensors | Predictive maintenance, efficiency gains |
| Government | Census data, surveillance, public records | Smart cities, disaster management |
Importance of Big Data in Decision-Making
The growing importance of Big Data lies in its ability to turn raw information into actionable insights. Decision-makers across industries rely on Big Data analytics for:
-
Enhanced Business Intelligence – Companies can analyze consumer preferences, buying habits, and market trends to improve marketing strategies.
-
Improved Efficiency – Real-time data allows organizations to optimize supply chains, monitor processes, and reduce costs.
-
Predictive Analytics – Businesses use historical data to forecast demand, market trends, and customer behavior.
-
Better Customer Experiences – Personalization through data-driven recommendations enhances customer satisfaction.
-
Risk Management – Identifying fraudulent activity, cybersecurity threats, or financial risks is easier with Big Data analytics.
Graph : Global Data Generated Over Time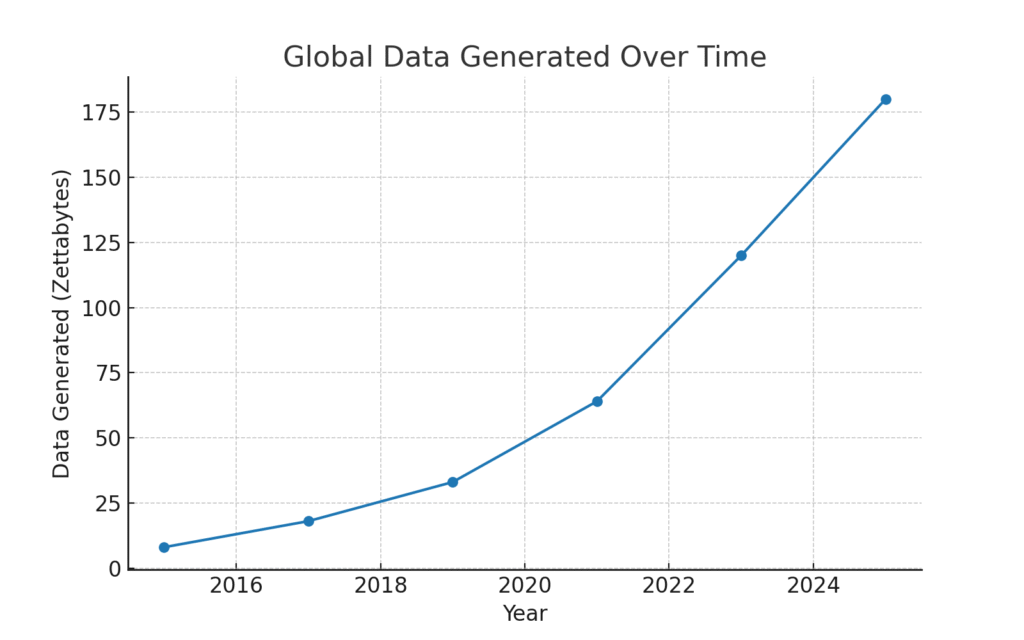
Big Data is generated from multiple channels, which can be categorized into three main types:
-
Human-generated data – Social media posts, online reviews, emails, photos, and videos.
-
Machine-generated data – Sensor readings, IoT device logs, GPS tracking, and industrial machinery output.
-
Transactional data – Financial transactions, online purchases, and point-of-sale data.
Table 2: Comparison Between Traditional Data and Big Data
| Feature | Traditional Data | Big Data |
|---|---|---|
| Size | MBs to GBs | TBs to PBs and beyond |
| Storage | Relational Databases (SQL) | Distributed Storage (Hadoop, NoSQL) |
| Processing | Batch processing | Real-time & parallel processing |
| Data Type | Mostly structured | Structured, semi-structured, unstructured |
| Analysis Tools | Excel, SQL | Spark, Hadoop, AI & ML-based tools |
Benefits of Big Data
-
Better Decision-Making – Real-time insights help leaders make informed choices.
-
Cost Savings – Optimizing operations through predictive analysis reduces inefficiencies.
-
Competitive Advantage – Businesses leveraging Big Data stay ahead in the market.
-
Enhanced Security – Big Data analytics helps detect fraud and cyber threats.
-
Innovation – Companies use data-driven insights to design new products and services.
Challenges of Big Data
Despite its potential, Big Data also poses several challenges:
-
Data Privacy & Security – Safeguarding sensitive data against breaches is a top concern.
-
Storage & Management – The huge volume of data requires advanced infrastructure.
-
Data Quality – Inaccurate or incomplete data leads to wrong insights.
-
Skill Gap – There is a shortage of skilled professionals in Big Data analytics.
-
High Costs – Implementing Big Data systems can be expensive for small businesses.

Real-World Applications of Big Data
1. Healthcare
Big Data enables early disease detection, personalized treatment, and efficient hospital management. For example, predictive analytics helps forecast flu outbreaks based on social media and hospital reports.
2. Banking & Finance
Financial institutions use Big Data for fraud detection, customer profiling, and risk assessment. Real-time data analysis identifies unusual spending patterns instantly.
3. Retail & E-commerce
Amazon and Netflix use recommendation algorithms powered by Big Data to suggest products and shows based on user history.
4. Education
Universities analyze student performance data to personalize learning and improve retention rates.
5. Government & Smart Cities
Governments use Big Data for traffic management, crime prediction, and resource allocation in smart cities.
Future of Big Data
The future of Big Data is closely linked with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). As organizations move toward automation, Big Data will provide the fuel for training AI models. Additionally, edge computing and cloud-based solutions will make data processing faster and more efficient. Big Data will also play a crucial role in climate change research, autonomous vehicles, blockchain applications, and personalized medicine.
Conclusion
Big Data is no longer just a trend; it is the backbone of modern decision-making and innovation. By collecting, analyzing, and interpreting massive datasets, businesses, governments, and organizations can unlock valuable insights that drive efficiency, growth, and sustainability. However, with great power comes great responsibility. Organizations must address privacy, ethical, and security concerns while implementing Big Data strategies. In the future, as technologies continue to evolve, Big Data will remain at the center of digital transformation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Big Data in simple terms?
Big Data refers to extremely large and complex sets of data that cannot be handled with traditional tools like spreadsheets or basic databases. It includes information from social media, sensors, transactions, and machines, which when analyzed provides useful insights.
Why is Big Data important?
Big Data is important because it helps businesses, governments, and organizations make better decisions. It allows them to predict trends, understand customer behavior, improve efficiency, reduce risks, and create new opportunities.
What are the main characteristics of Big Data?
Big Data is often explained using the 5 V’s:
-
Volume (large amount of data)
-
Velocity (speed of data generation)
-
Variety (different formats of data)
-
Veracity (accuracy and reliability)
-
Value (usefulness of insights gained)
What technologies are used in Big Data?
Some popular technologies include Hadoop, Apache Spark, MongoDB, Cassandra, and NoSQL databases, along with cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. Machine Learning and AI are also widely used in Big Data analytics.
What are the biggest challenges in Big Data?
The main challenges are data privacy, security risks, storage issues, high costs, lack of skilled professionals, and maintaining data quality.
Which industries benefit the most from Big Data?
Industries such as healthcare, finance, e-commerce, manufacturing, education, and government benefit significantly from Big Data by using predictive analytics, fraud detection, customer personalization, and operational efficiency.
How is Big Data different from traditional data?
Traditional data is usually smaller in size, structured, and stored in relational databases. Big Data, on the other hand, includes structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, stored in distributed systems, and analyzed using advanced tools.
What is the future of Big Data?
The future of Big Data lies in its integration with AI, Machine Learning, cloud computing, and IoT. It will be critical for innovations in smart cities, personalized medicine, climate change solutions, and autonomous vehicles.




