What is a Proxy Server? A Beginner’s Guide to Online Privacy
In today’s digital world, almost every action we take online leaves behind a trace. From browsing websites to streaming videos and even making online payments, our activities generate data. This data can be collected, tracked, and sometimes misused. For this reason, people are becoming more aware of tools that help them maintain online privacy and security. One such tool is a proxy server.If you’ve ever wondered what a proxy server is, how it works, and why you might need one, this guide will walk you through the basics in an easy-to-understand way.
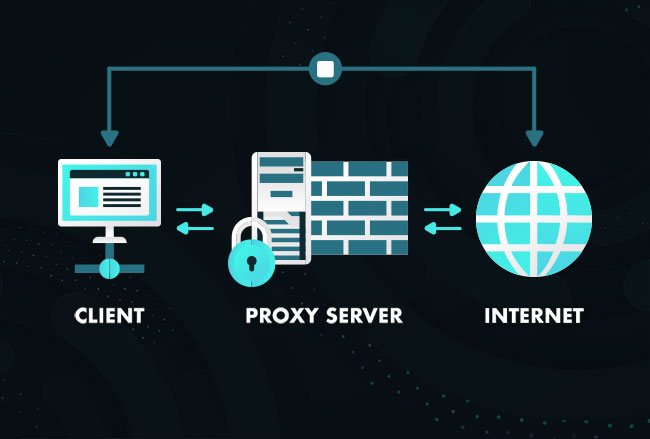
What is a Proxy Server?
A proxy server is an intermediary between your computer (or device) and the internet. Instead of directly connecting to a website, your request first goes to the proxy server, which then forwards it to the destination site. Once the website responds, the proxy sends the data back to you.In simple words, think of a proxy server as a middleman. Instead of revealing your actual identity online, it masks it with its own.
Example:
Without a proxy → You → Website (website sees your IP address).
With a proxy → You → Proxy server → Website (website sees the proxy’s IP address, not yours).
Why Do People Use Proxy Servers?
Proxy servers offer a range of benefits. Here are some common reasons people use them:
1. Enhanced Privacy
When browsing through a proxy, your real IP address is hidden. This makes it harder for websites, advertisers, or cybercriminals to track your online behavior.
2. Bypassing Geo-Restrictions
Some websites, videos, or online services are blocked in certain countries. With a proxy server located in another region, you can access content as if you were browsing from there.
3. Improved Security
Some proxies provide an extra layer of security by filtering malicious content, blocking suspicious websites, or hiding your identity from potential attackers.
4. Faster Browsing (Caching)
Proxies can cache (store) copies of websites. If many users request the same site, the proxy can serve the stored version, reducing load times and saving bandwidth.
5. Control and Monitoring
Organizations use proxies to control employee internet use. For instance, schools may use proxies to block adult content, while companies can monitor internet activity to ensure productivity.
How Does a Proxy Server Work?
The process of using a proxy can be broken down into simple steps:
-
You send a request (like opening YouTube).
-
The request goes to the proxy server.
-
The proxy forwards the request to YouTube on your behalf.
-
YouTube sends back the video data to the proxy.
-
The proxy delivers it to your device.
This ensures the website never directly communicates with your actual device—it only interacts with the proxy.
Types of Proxy Servers
Not all proxies are the same. Here are the most common types:
1. Forward Proxy
-
The standard proxy type used by individuals.
-
Protects the user by acting as a shield between them and the internet.
2. Reverse Proxy
-
Used by websites or servers to protect themselves from direct exposure.
-
Often placed in front of servers to balance traffic and improve security.
3. Transparent Proxy
-
Reveals that it’s a proxy and often still passes your IP.
-
Commonly used by institutions like schools or public Wi-Fi providers.
4. Anonymous Proxy
-
Hides your IP address but lets websites know you are using a proxy.
5. High-Anonymity Proxy (Elite Proxy)
-
Completely hides both your IP and the fact that you’re using a proxy.
-
Best for privacy-conscious users.
6. Distorting Proxy
-
Provides a fake IP address to websites, misleading them about your location.
Proxy Server vs. VPN: What’s the Difference?
Many people confuse proxies with VPNs (Virtual Private Networks). While both provide privacy, they are not the same.
-
Proxy Server:
-
Works on the application level (e.g., web browser).
-
Masks your IP address.
-
Doesn’t usually encrypt traffic.
-
-
VPN:
-
Works on the system level (all internet traffic).
-
Encrypts your data fully.
-
Offers stronger privacy and security.
-
If your main goal is bypassing geo-blocks or masking your IP, a proxy is often enough. But if you want complete online privacy, a VPN may be the better choice.
Benefits of Using a Proxy Server
-
Keeps your browsing private.
-
Helps you access blocked websites or restricted content.
-
Protects against certain cyber threats.
-
Useful for businesses to manage employee activity.
-
Can reduce internet costs with caching.
Risks and Limitations of Proxy Servers
While proxies are helpful, they aren’t perfect. Some risks include:
-
No encryption → Your data may still be visible to hackers or ISPs.
-
Free proxies may be unsafe → Some free proxies steal user data.
-
Slower speeds → If too many people use the same proxy, performance drops.
-
Not foolproof → Advanced websites may detect and block proxy traffic.
Real-Life Uses of Proxy Servers
-
Students use proxies to access websites blocked by schools.
-
Employees rely on them to securely access company networks remotely.
-
Businesses use proxies for web scraping and market research.
-
Everyday users use proxies to watch Netflix shows from other countries.
Tips for Choosing a Good Proxy Server
-
Pick a trusted provider (avoid shady free proxies).
-
Choose the right type based on your needs (anonymous, elite, reverse, etc.).
-
Look for speed and reliability (low latency, high uptime).
-
Consider whether you need dedicated proxies (for business) or shared proxies (cheaper, casual use).
The Future of Proxy Servers in Online Privacy
As digital privacy becomes a global concern, proxy servers will continue to evolve. They may integrate with AI-based filtering, stronger encryption, and multi-layered security systems. In combination with VPNs and other privacy tools, proxies will remain an essential option for people who want control over their online identity.
Conclusion
A proxy server is more than just a middleman—it’s a powerful tool for privacy, security, and freedom online. Whether you want to hide your IP address, access blocked content, or manage internet use in an organization, proxies offer flexible solutions.However, they’re not perfect and should be used wisely. For casual privacy needs, proxies are sufficient. But for complete protection, combining a proxy with other tools like VPNs, firewalls, and strong cybersecurity practices is the best way forward.In short: If you value online freedom and want to safeguard your digital identity, learning to use a proxy server is a great step toward safer browsing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. What exactly is a proxy server?
A proxy server is an intermediary between your device and the internet. It forwards your requests to websites and returns the responses, hiding your real IP address.
Q2. How does a proxy server protect my privacy?
By masking your IP address, a proxy server makes it harder for websites, advertisers, and hackers to track your real location or identity.
Q3. Is a proxy server the same as a VPN?
No. A VPN encrypts all your internet traffic and works system-wide, while a proxy usually works for specific apps or browsers and doesn’t always encrypt your data.
Q4. Can I use a proxy server to access blocked websites?
Yes. Proxies are often used to bypass geo-restrictions or censorship, allowing you to access content not available in your country.
Q5. Are free proxy servers safe to use?
Not always. Many free proxies log your activity or sell your data. It’s safer to use a trusted paid service or a proxy provided by your organization.
Q6. What types of proxy servers exist?
Common types include forward proxies, reverse proxies, anonymous proxies, high-anonymity (elite) proxies, transparent proxies, and distorting proxies. Each serves different privacy and security needs.
Q7. Do proxy servers slow down internet speed?
They can. If the proxy is overloaded with users or poorly configured, your browsing speed may decrease. High-quality proxies usually maintain good speeds.
Q8. Can businesses benefit from using proxy servers?
Yes. Companies use proxies for employee monitoring, securing internal systems, balancing server traffic, and conducting market research through web scraping.
Q9. Do proxy servers encrypt my data?
Most proxies do not encrypt your data. If you need encryption, consider using a VPN in addition to or instead of a proxy.
Q10. What devices can use proxy servers?
Proxies can be configured on computers, smartphones, tablets, or even entire networks, depending on your needs.
Q11. Are proxy servers legal?
Yes, proxies are legal in most countries. However, using them for illegal activities—such as hacking, piracy, or fraud—remains against the law.
Q12. How do I choose the best proxy server?
Look for reliability, speed, security, and the right level of anonymity. Paid proxies from trusted providers are generally safer than free options.




