Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing: Future of Data Processing
In our fast-moving digital world, the demand for faster processing, real-time analytics, and seamless connectivity has grown dramatically. Two technologies that are shaping the future of data computing are Edge Computing and Cloud Computing. While both play essential roles in managing and processing data, they differ in architecture, speed, cost, and purpose. This article explores the core differences between edge computing and cloud computing, their advantages, use cases, and which one might be better depending on your business needs.
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to delivering computing services including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics over the internet. These services are hosted in data centers operated by companies like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. Instead of storing data on local machines, users can access it from any device connected to the internet.
Key features of cloud computing
-
Centralized data processing
-
High scalability and flexibility
-
Pay-as-you-go pricing
-
Global access
What Is Edge Computing?
Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation such as sensors, smartphones, or IoT devices. Rather than sending all data to a cloud server, edge computing processes data locally or at the “edge” of the network. This significantly reduces latency and bandwidth usage.
Key features of edge computing
-
Decentralized data processing
-
Real-time response
-
Reduced reliance on central servers
-
Greater data privacy in some cases
Key Differences Between Edge and Cloud Computing
To better understand the contrast, here is a breakdown of the major differences between the two computing models:
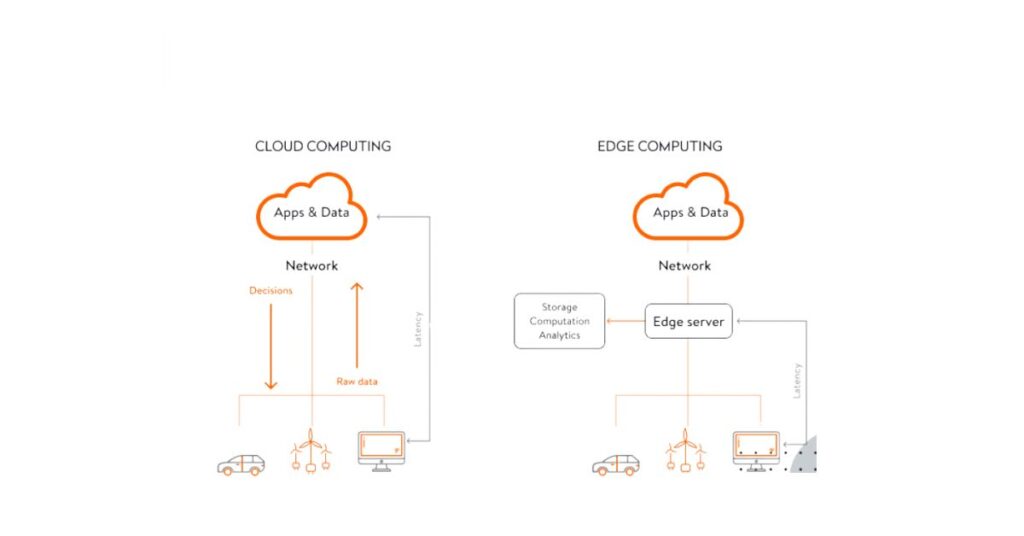
1. Location of Data Processing
-
Cloud computing processes data in centralized data centers that may be far from the user or device.
-
Edge computing processes data at or near the device where it is generated.
2. Latency
-
Cloud computing can introduce delays because data must travel over the internet.
-
Edge computing minimizes latency by processing data locally.
3. Bandwidth Use
-
Cloud computing can require a lot of bandwidth to transfer data to and from the cloud.
-
Edge computing reduces bandwidth needs by filtering and processing data locally.
4. Reliability
-
Cloud computing depends heavily on internet connectivity. If the network is down, access to cloud services can be interrupted.
-
Edge computing can function independently of the internet, improving system reliability in remote or offline environments.
5. Security and Privacy
-
Cloud computing may expose sensitive data during transmission and while stored in data centers.
-
Edge computing processes data closer to its source, which can reduce exposure to cyber threats, but it also increases the number of endpoints to secure.
6. Scalability
-
Cloud computing is highly scalable due to the virtually unlimited resources of cloud providers.
-
Edge computing is limited in scale by local device resources and may require multiple edge nodes for broader deployments.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has dominated the enterprise IT space for over a decade due to its many benefits.
Cost Efficiency
Cloud services follow a pay-as-you-use model, which is cost-effective for businesses that do not want to invest in physical hardware.
Accessibility
With cloud computing, data and applications are accessible from anywhere in the world through the internet.
Scalability
It allows businesses to scale up or down based on demand, ensuring flexibility during peak and off-peak times.
Disaster Recovery
Cloud providers offer backup and recovery solutions, reducing the risk of data loss.
Advantages of Edge Computing
Edge computing is gaining popularity because of the rise in connected devices and real-time data processing needs.
Real-Time Data Processing
Edge computing is ideal for applications where milliseconds matter, such as autonomous vehicles or smart manufacturing.
Lower Latency
By processing data locally, edge computing delivers faster response times and improved performance.
Reduced Bandwidth Costs
Only relevant or filtered data is sent to the cloud, saving bandwidth and reducing operational costs.
Better Privacy and Security in Some Cases
Sensitive data can be processed on-site, reducing exposure to network-based attacks.
Use Cases of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing supports a wide variety of business and consumer applications.
Enterprise Applications
Cloud computing powers CRM systems like Salesforce, HR platforms, and business analytics tools.
Web Hosting and Storage
Popular websites and apps use the cloud for hosting, file storage, and backups.

Big Data and AI
Massive datasets used in machine learning and artificial intelligence are processed in the cloud due to its computing power.
Remote Work and Collaboration
Tools like Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, and Zoom are cloud-based, enabling global teams to collaborate easily.
Use Cases of Edge Computing
Edge computing is designed for time-sensitive, data-heavy, or remote environments.
Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars rely on real-time processing to make split-second decisions, which edge computing enables.
Smart Cities
Traffic lights, surveillance systems, and public utilities use edge computing for local, real-time decision-making.

Healthcare Devices
Wearable monitors and remote surgery tools use edge computing to ensure fast response and reliability.
Industrial IoT (IIoT)
Factories use edge devices to monitor equipment performance and predict failures before they happen.
Edge vs Cloud: Which One to Choose?
Both edge and cloud computing have their strengths, and often they work best together in a hybrid model.
Choose cloud computing if you need:
-
Centralized management
-
High scalability
-
Access from anywhere
-
Cost-effective data storage
Choose edge computing if you need:
-
Ultra-low latency
-
Local processing
-
Offline capabilities
-
Real-time analytics
For example, a security camera may use edge computing to detect motion and only send footage to the cloud if it senses a threat. This hybrid approach saves bandwidth and provides real-time alerts.
Future Trends in Edge and Cloud Computing
1. Growth of IoT Devices
As more devices get connected, edge computing will become essential to handle the volume of data generated locally.
2. AI at the Edge
Artificial Intelligence is being integrated into edge devices to enable smart decision-making without relying on the cloud.
3. 5G Integration
The rollout of 5G networks will accelerate edge computing by enabling faster data transfer between devices and local nodes.
4. Hybrid Cloud-Edge Models
More organizations are adopting hybrid strategies, combining edge computing with cloud infrastructure for optimal results.
Challenges of Cloud and Edge Computing
Challenges in Cloud Computing
-
Downtime due to network issues
-
Data privacy concerns
-
Vendor lock-in with service providers
Challenges in Edge Computing
-
Security of multiple endpoints
-
Higher upfront hardware costs
-
Complexity in managing distributed systems
Security Considerations
Cloud Security
-
Cloud providers invest heavily in security infrastructure.
-
Data encryption and compliance are standard, but businesses must also secure their access and credentials.
Edge Security
-
Edge devices can be vulnerable to attacks if not properly protected.
-
Physical security, firmware updates, and endpoint monitoring are essential.
Both systems require comprehensive security strategies tailored to their architecture.
Industry Adoption Examples
Retail
Retailers use edge computing in stores for digital signage, customer behavior tracking, and real-time inventory updates.
Healthcare
Hospitals use cloud storage for patient records and edge devices for monitoring patients in real-time.
Agriculture
Smart farming uses edge computing for soil and weather sensors while cloud platforms analyze long-term data trends.
Final Thoughts
Edge computing and cloud computing are not mutually exclusive. In fact, their combination can bring out the best in both worlds. Cloud computing offers unmatched scalability and global accessibility, while edge computing ensures real-time processing and low-latency responses.
FAQs
What is the main difference between cloud and edge computing
Cloud computing processes data at centralized locations. Edge computing handles it close to where it is generated.
Is edge computing replacing cloud computing
No. Edge computing is used alongside cloud computing in many systems. They complement each other.
Is edge computing more secure
It can be more private since data stays local. However, it requires strong security at each device.
Can edge computing work offline
Yes. It can function without internet, which makes it ideal for remote or disconnected environments.
Which industries benefit most from edge computing
Industries like healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, and smart cities benefit from real time data processing.




